Business provision is ultimately about creating sustainable value, where value is the measure of net benefit
(or worth ) gained against cost.
In other words we may say “value is how much a benefit is worth”.
This applies both ways - for the customer and for the business provider |
•
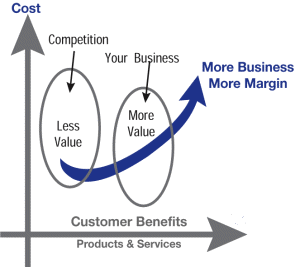
Customer’s perception of competitive benefit
drives market environments.
•
The balance between cost of provision and
market environments drives business value.
•
For services operating in monopoly situations
( e.g. Government provision )
poor value is reflect by constituent dissatisfaction.
|
|
| |
|
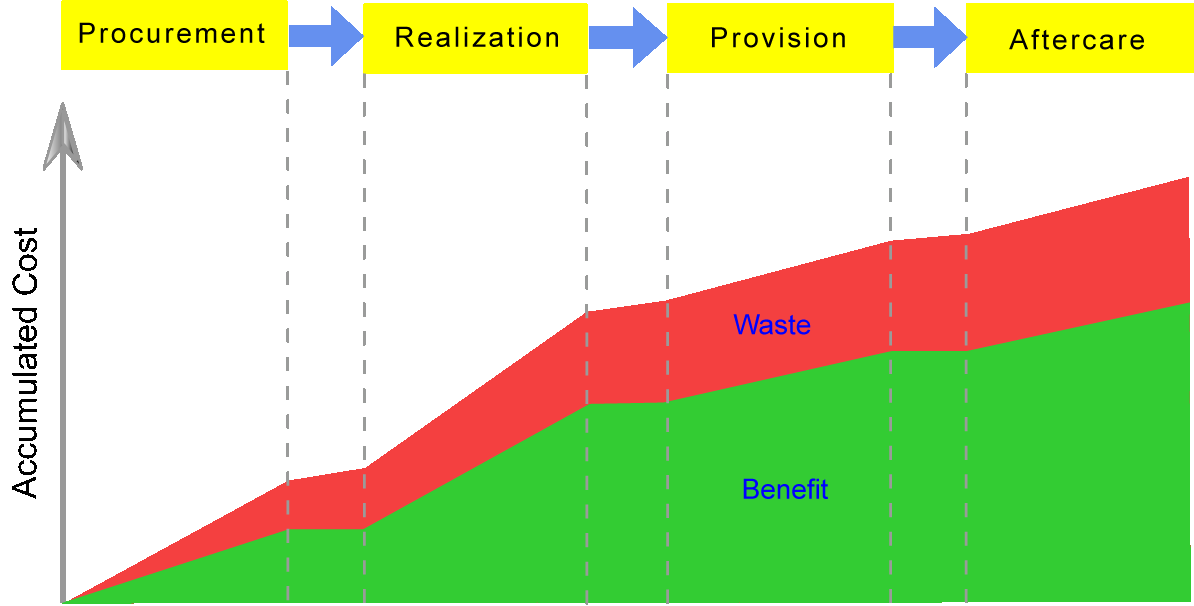
To improve value organizations need to look along the value creation chain
|
| |
 |
| |
The most effective way to improve value is to decrease waste
This leads to reducing costs while retaining benefits |
| |
|
Waste |
Waste has two components:
•
Inefficiency
•
Deficiency
Waiting time is an example of inefficiency.
Repair is an example of deficiency.
|
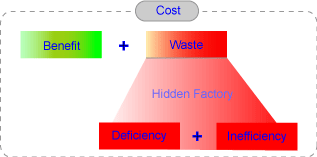 |
We may call waste
“The Hidden Factory”
for waste generally remains undetected while
consuming a sizable amount of all the same resources used for the
creation of benefit ( value ).
The causes of waste are manifold:
They range from design of "product" & process and inadequate communication
through to incompetence and even negligence.
Waste is apparent in both the physical
processes (operational processes)as well as the intangible processes
(transactional processes).
Indeed most waist today, in manufacturing and
service organizations, occurs in their transactional processes and hidden by
the ineptitudes of conventional accounting systems.
|